Miklós Molnár1
- Division of Structural Engineering, Lund University, P.O. Box 118, 221 00 Lund, Sweden, miklos.molnar@kstr.lth.se
ABSTRACT
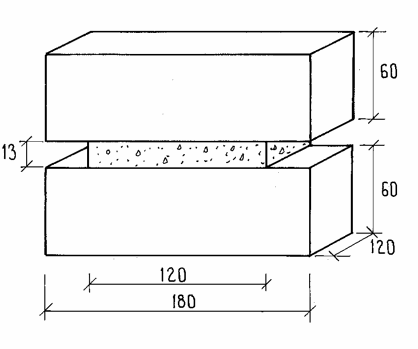
The influence of mortar type on the shear behaviour of bed joints subjected to simultaneous shear and normal pre-compression was investigated. The test specimens were manufactured of solid clay bricks combined with a typically strong, cement rich respectively a typically weak, lime rich mortar. The tests were carried out under deformation control, which enabled both the elastic and softening plastic properties of the joints to be observed. The elastic shear deformation of the joints with the weak mortar was 2-4 times larger than in the case with the strong mortar. Joints with the weak mortar exhibited less pronounced shear softening than the joints with the strong mortar. Results of the investigations suggest that a shift from the strong to the weak mortar might improve the resistance to cracking of a horizontally restrained wall by 30-60%.
Key words: Masonry, mortar, cement, lime, shear, strength, deformation, dilatancy.
MORJTS01