Ahmed Elsaadawy, Mahmoud Elsayed, Clayton Pettit, and Carlos Cruz-Noguez
i Ph.D. Student, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, elsaadaw@ualberta.ca
ii Ph.D. Student, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, mhelsaye@ualberta.ca
iii Assistant Professor, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, cpettit@ualberta.ca
iv Professor, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, cruznogu@ualberta.ca
ABSTRACT
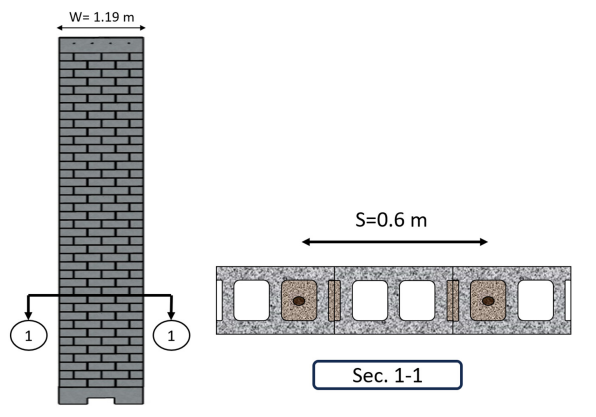
Slender masonry walls with a slenderness ratio exceeding 30 are commonly used in single-story buildings in Canada. However, the design of these walls is subject to strict limits and requirements under the Canadian masonry standard (CSA S304-24), which can affect their capacity. One way to increase wall capacity and reduce the amount of reinforcement and grout used in conventional reinforcement masonry walls is by using high-strength reinforcement (HSR). High-strength reinforcement (HSR) are widely used in concrete standards such as (ACI 318-24) and (CSA A23.3:24). However, masonry standards such as (CSA S304- 24) and (TMS 402/602-22) prohibit the use of high-strength reinforcement in all structural elements including beams, walls, and columns. Due to the limited information on this topic, this research aims to study the effects of detailing slender masonry walls with high-strength reinforcement. A numerical simulation was used to predict the expected out-of-plane performance of slender masonry walls with high-strength reinforcement and conventional steel. The same height-to-thickness ratio, loads, and boundary conditions were used to compare their performance. A parametric analysis was conducted to examine the effects of key parameters, including bar yield strength, block thickness, and bar diameter, on the flexural capacity of slender masonry walls. The results indicate that an increase in bar yield strength leads to a corresponding enhancement in the flexural capacity of the walls.
KEYWORDS: slender masonry walls, high strength reinforcement, analysis model, flexural capacity.
022-Elsaadawy.pdf