Zeeshan Manzoor Bhat and Yogendra Singh
i Research Scholar, Department of Earthquake Engineering, IIT Roorkee, Roorkee, India, zbhat@eq.iitr.ac.in
ii Professor, Department of Earthquake Engineering, IIT Roorkee, Roorkee, India, yogendra.singh@eq.iitr.ac.in
ABSTRACT
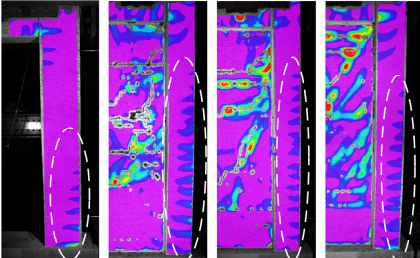
This paper investigates the cyclic behavior of reinforced concrete (RC) frames with various types of masonry infills: burnt clay bricks, fly ash bricks, and autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) blocks. The RC frames were designed in compliance with the latest provisions of the Indian seismic code. To assess the impact of masonry infills, four specimens-one bare frame and three masonry infilled frames-were subjected to cyclic loading. Digital Image Correlation (DIC) was employed to provide a detailed analysis of damage progression throughout the testing process. The study focused on key parameters such as stiffness, strength, and energy dissipation, and a comparison with available analytical models was conducted. Infilled frames were found to exhibit greater stiffness, strength, and energy dissipation compared to the bare frame. Due to the seismic code-compliant design, a ductile failure mode was observed in both the bare and infilled frames. The experimental results showed good agreement with certain analytical models regarding strength and stiffness. The infills restrained deformation at the base of the surrounding columns, resulting in dispersed flexural cracks in the columns, while cracks in the bare frame columns were concentrated at the base.
KEYWORDS: AAC block, cyclic testing, DIC, fly ash brick, masonry infill, RC frame.
121-Bhat.pdf