Tesfaalem Gereziher Atsbha, Wei Victor Liu, and Yuxiang Chen
i Grad Research Asst Fellowship, Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada, atsbha@ualberta.ca
ii Associate Professor, Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada, victor.liu@ualberta.ca
iii Associate Professor, Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada, yuxiang.chen@ualberta.ca
ABSTRACT
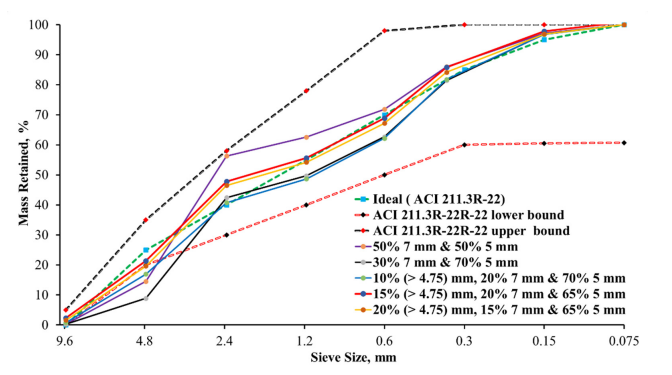
The masonry industry worldwide is seeking thermally efficient masonry materials, sustainable manufacturing and construction practices, and the integration of these technologies. Belite Calcium Sulfoaluminate (BCSA)-based concrete offers a promising solution, with benefits such as a 34–48% reduction in carbon footprint, rapid strength development, reduced drying shrinkage, and enhanced durability. This study is the first part of research program that aims to develop new BCSA-based concrete mixtures to produce high-performance concrete masonry units (CMUs) and assess their early-age mechanical properties and dimensional stability. The study presents a review of CSA-based concrete and describes an ASTM- and ACI-based aggregate preparation process for normal-weight CMU production, following ACI 211 grading guidelines. The well-graded particle distribution, characterized by a fineness modulus (FM) of 3.79, is expected to enhance packing density, minimize voids, and improve mechanical performance. A carefully designed cement-aggregate mix was developed to balance cement content, water-to-cement ratio, and aggregate proportions for optimal fresh and hardened properties. An experimental approach following ASTM standards will systematically evaluate material properties and mixture performance based on lab-scale samples. Expected outcomes, which will be presented at the conference, include improved early-age mechanical properties, enhanced dimensional stability, reduced curing time, and lower production costs by minimizing reliance on energy-intensive processes, such as high-temperature and high-pressure steam curing, typically used to accelerate early strength gain, contributing to a lower-carbon CMU manufacturing process.
KEYWORDS: belite calcium Sulfoaluminate cement, concrete masonry units, durability, mechanical properties, sustainable construction, thermal performance.
159-Atsbha.pdf