Madalena Ponte, Gabriele Guerrini, Andrea Penna, and Rita Bento
i Postdoctoral Researcher, University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy, madalena.ponte@unipv.it
ii Assistant Professor, University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy, gabriele.guerrini@unipv.it
iii Full Professor, University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy, andrea.penna@unipv.it
iv Full Professor, CERIS, Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal, rita.bento@tecnico.ulisboa.pt
ABSTRACT
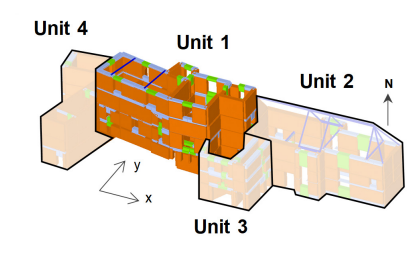
Rubble stone monuments, common in Mediterranean countries, are particularly vulnerable to seismic activity due to their construction techniques and materials. These structures typically consist of irregular, uncut stones, loosely bound with weak mortar, resulting in low tensile strength and poor cohesion. In addition, these historical structures are usually built as irregular aggregates, contributing to their earthquake vulnerability. Due to their cultural importance, in addition to safety and economic reasons, it is of utmost importance to perform accurate seismic assessments of historical masonry structures to preserve them. Most of the time, however, it is not easy for engineers to consider the interactions between different structural units in the aggregate, especially when it is difficult to define these units themselves. The National Palace of Sintra, located in Sintra, Portugal, is a representative example of irregular, largescale rubble stone monuments built in aggregate without previous planning. This paper presents an overview of the study conducted on the Palace, including the historical research and experimental campaign carried out to perform its seismic assessment. The equivalent frame numerical modeling of such a complex case study is also discussed, focusing on the interaction between the structural units. This modeling strategy was chosen due to the limited number of parameters required, which makes it one of the preferred methods within the practitioners’ community.
KEYWORDS: historical aggregates, interactions between buildings, equivalent frame modeling, nonlinear static analyses.
086-Ponte.pdf