Karren Izquierdo, Carlos Cruz-Noguez and Arash Mohsenijam
Karren Izquierdo, MSc student, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Alberta, 116 St & 85 Ave, Edmonton, AB, Canada, knhudson@ualberta.ca
Carlos Cruz-Noguez, Assistant Professor, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Alberta, 116 St & 85 Ave, Edmonton, AB, Canada, cruznogu@ualberta.ca
Arash Mohsenijam, Project Engineer, Supreme Group, 28169 96 Ave NW, Acheson, AB, Canada, mohsenij@ualberta.ca
ABSTRACT
The behaviour of partially grouted masonry shear walls is complex due to their anisotropic nature and the nonlinear interactions between blocks, mortar, grouted cells, ungrouted cells and steel
reinforcement. It is crucial to develop a greater understanding in this area, as sudden shear failures of masonry walls can lead to catastrophic losses of human life and property.
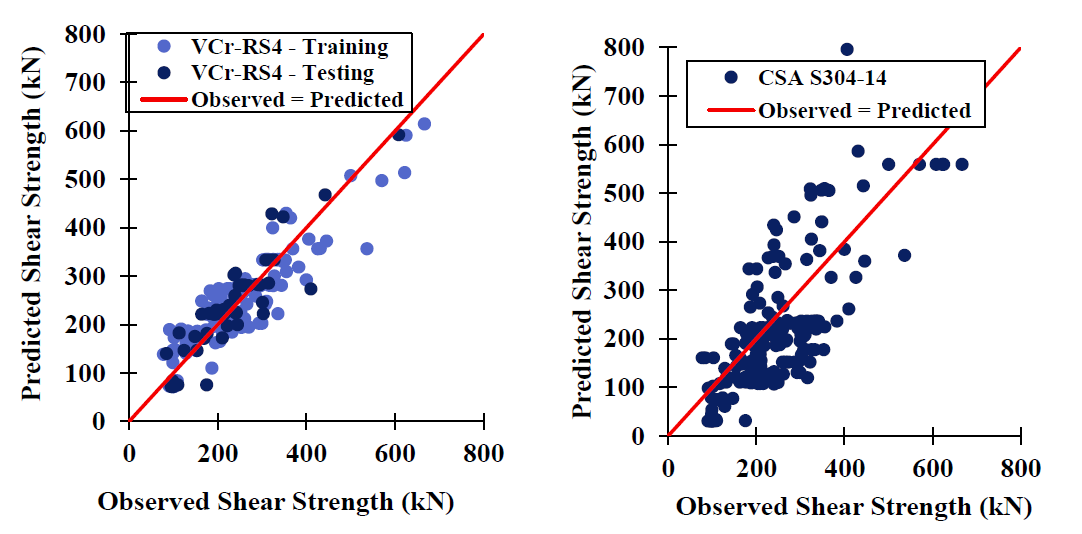
This study presents the development of several new in-plane shear strength models for partially grouted masonry walls using stepwise regression. Stepwise regression identifies the most
significant input variables from a pool of candidates, eliminating interdependencies and reducing the pool to an appropriate subset for predicting the output variable. The models were generated using data compiled from 292 experimentally tested partially grouted masonry shear walls. The stepwise regressions were found to significantly outperform other existing shear strength models. It was found that, of the variables studied, the most significant ones for estimating the shear strength of partially grouted masonry walls are the axial load, wall geometry, compressive strength of mortar, and area of interior vertical reinforcement.
KEYWORDS: partially grouted, prediction models, shear strength, stepwise regression